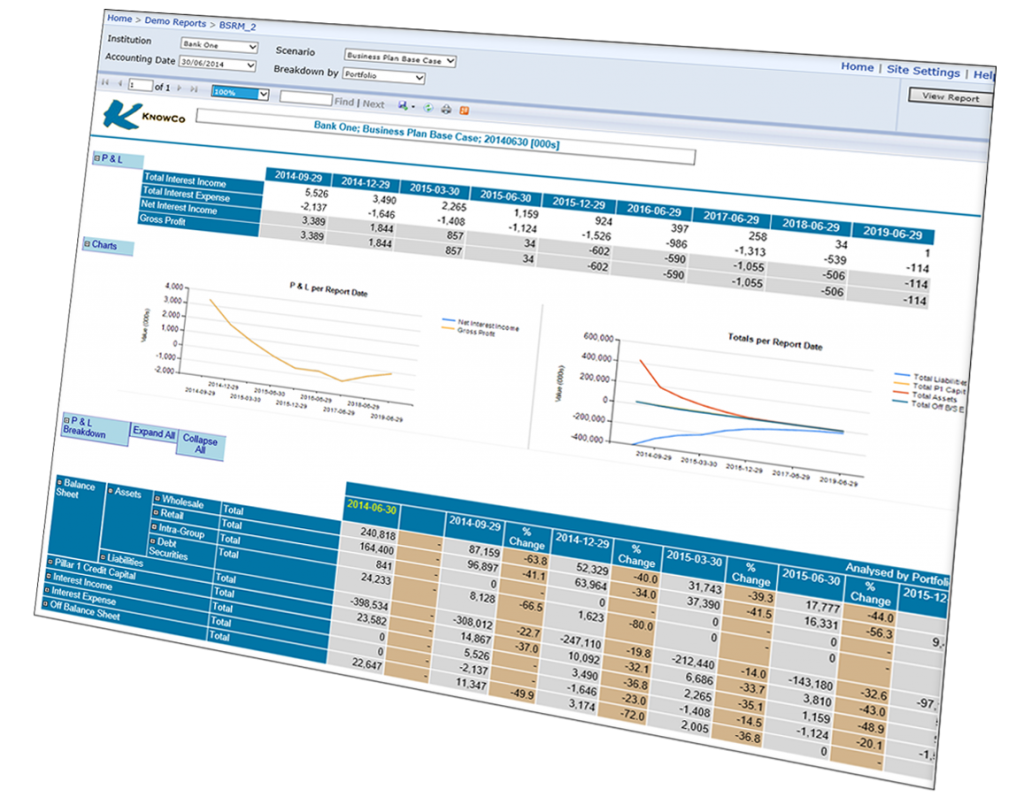
Basel III is a third version of Basel Accord. It establishes international standards for banks regarding capital adequacy, stress tests, and liquidity. Basel II was more concerned with the capital structure. Basel III is more comprehensive, and includes several new regulations. These regulations are applicable to all banks, big and small. Ask your bank's chief executive if you have questions about Basel III. He or she will be more than happy to help you.
Capital contingent forms
Contingent Forms of Capital (CFSs), are an option for troubled institutions to raise capital using debt securities that convert into equity at prearranged conditions. These instruments can reduce the debt-to–equity ratios, and can be used to recapitalize institutions without insolvency proceedings.
Banks can use CFSs to comply with Basel III requirements. These rules require banks to maintain a minimum capital ratio of 10%. These banks must have enough Tier 1 capital, in other words, to deal with extreme circumstances and limit the damage from bad loans.
Leverage ratio
The Basel III framework's most important measure for banks is the leverage ratio. It is calculated as the sum of the bank's total exposure and its supervisory Tier 1 capital. A low leverage rate means the bank is not experiencing capital stress. However, a high ratio can indicate that the bank has experienced stress. To determine the ratio, the valuation of balance sheet items must be done in accordance with the applicable accounting standards.
Leverage ratios must be disclosed publicly. Under the regulations, banks are required to report their leverage ratios quarterly. G-SIBs will be required to report their leverage ratios every quarter beginning June 2021.
Transition periods
Basel III is a set new requirements that will impact banks worldwide. The agreement has certain requirements that all banks must meet, and it also sets transitional periods for the implementation of the standards. The new requirements are minimized by the transition periods. However, the new rules are likely to have a significant impact when fully implemented. We'll be looking at Canada's specific requirements in this article.
Basel III will mandate that banks comply with certain minimum capital ratios. Each of these minimum capital ratios will mandate that banks have certain levels of common equity or Tier 1 capital. New rules will require banks to keep more of their earnings as capital. The goal is to increase safety by requiring banks that they maintain higher capital levels in good periods.

Phase-ins
A number of issues will be at play during the implementation of Basel III. One of these issues is how to implement phase ins and outs. Basel Committee believes that the changes will have a minimal impact on the economy overall and that they will bring greater stability and safety to the system than their costs.
The risk-management indicator's sensitivity will be a significant issue. Basel III, which replaces the proxy indicator in its calculation, will make it more sensitive to operational and other risks. For the new indicator to be accurate, banks must have ten years worth of operational loss data. This new measure is only applicable to large banks and not small ones.
FAQ
What are the five management steps?
Each business has five stages: planning, execution and monitoring.
Planning involves setting goals for the future. Planning involves defining your goals and how to get there.
Execution occurs when you actually carry out the plans. It is important to ensure that everyone follows the plans.
Monitoring allows you to monitor your progress towards achieving your goals. Regular reviews should be done of your performance against targets or budgets.
Reviews take place at the end of each year. They allow for an assessment of whether all went well throughout the year. If not, it is possible to make improvements for next year.
Evaluation takes place after the annual review. It helps identify what worked well and what didn't. It also gives feedback on how well people did.
What is Six Sigma, exactly?
It's a strategy for quality improvement that emphasizes customer care and continuous learning. The goal is to eliminate defects by using statistical techniques.
Six Sigma was developed at Motorola in 1986 as part of its efforts to improve manufacturing processes.
The idea spread quickly in the industry. Today many organizations use six-sigma techniques to improve product design.
What is a management tool to help with decision-making?
A decision matrix is a simple but powerful tool for helping managers make decisions. It allows them to consider all possible solutions.
A decision matrix is a way to organize alternatives into rows and columns. This makes it easy to see how each alternative affects other choices.
We have four options in this example. They are represented by the boxes to the left of the matrix. Each box represents a different option. The top row depicts the current status quo, while the bottom row represents what would happen if no action was taken.
The effect of Option 1 can be seen in the middle column. It would increase sales by $2 million to 3 million in this instance.
The results of choosing Option 2 and 3 can be seen in the columns below. These positive changes result in increased sales of $1 million and $500,000. They also have negative consequences. For instance, Option 2 increases cost by $100 thousand while Option 3 reduces profits by $200 thousand.
The final column shows results of choosing Option 4. This results in a decrease of sales by $1,000,000
The best thing about using a decision matrix is that you don't need to remember which numbers go where. Simply look at the cells to instantly determine if one choice is better than the other.
This is because the matrix has done all the hard work. It's as easy as comparing numbers in the appropriate cells.
Here is an example how you might use the decision matrix in your company.
Decide whether you want to invest more in advertising. If you do, you'll be able to increase your revenue by $5 thousand per month. However, this will mean that you'll have additional expenses of $10,000.
You can calculate the net result of investing in advertising by looking at the cell directly below the one that says "Advertising." That number is $15 thousand. Advertising is more valuable than its costs.
What is the difference in Six Sigma and TQM?
The major difference between the two tools for quality management is that six Sigma focuses on eliminating defect while total quality control (TQM), on improving processes and decreasing costs.
Six Sigma can be described as a strategy for continuous improvement. It emphasizes the elimination and improvement of defects using statistical methods, such as control charts, P-charts and Pareto analysis.
This method attempts to reduce variations in product output. This is done by identifying and correcting the root causes of problems.
Total quality management includes monitoring and measuring all aspects of an organization's performance. Training employees is also part of total quality management.
It is often used as a strategy to increase productivity.
What is Kaizen and how can it help you?
Kaizen is a Japanese term for "continuous improvement." It encourages employees constantly to look for ways that they can improve their work environment.
Kaizen is a belief that everyone should have the ability to do their job well.
What does the term "project management” mean?
Management is the act of managing activities in order to complete a project.
These include planning the scope and identifying the needs, creating the budget, organizing the team, scheduling the work and monitoring progress. Finally, we close down the project.
What does Six Sigma mean?
Six Sigma uses statistics to measure problems, find root causes, fix them, and learn from past mistakes.
The first step in solving a problem is to identify it.
The next step is to collect data and analyze it in order to identify trends or patterns.
Then corrective actions are taken to solve the problem.
The data are then reanalyzed to see if the problem is solved.
This cycle continues until there is a solution.
Statistics
- The BLS says that financial services jobs like banking are expected to grow 4% by 2030, about as fast as the national average. (wgu.edu)
- The average salary for financial advisors in 2021 is around $60,000 per year, with the top 10% of the profession making more than $111,000 per year. (wgu.edu)
- UpCounsel accepts only the top 5 percent of lawyers on its site. (upcounsel.com)
- Your choice in Step 5 may very likely be the same or similar to the alternative you placed at the top of your list at the end of Step 4. (umassd.edu)
- Hire the top business lawyers and save up to 60% on legal fees (upcounsel.com)
External Links
How To
How is Lean Manufacturing done?
Lean Manufacturing uses structured methods to reduce waste, increase efficiency and reduce waste. They were developed by Toyota Motor Corporation in Japan during the 1980s. The main goal was to produce products at lower costs while maintaining quality. Lean manufacturing eliminates unnecessary steps and activities from a production process. It is made up of five elements: continuous improvement, continuous improvement, just in-time, continuous change, and 5S. Pull systems allow customers to get exactly what they want without having to do extra work. Continuous improvement is constantly improving upon existing processes. Just-in time refers to components and materials being delivered right at the place they are needed. Kaizen means continuous improvement. Kaizen involves making small changes and improving continuously. Fifth, the 5S stand for sort, set up in order to shine, standardize, maintain, and standardize. These five elements work together to produce the best results.
Lean Production System
Six key concepts are the basis of lean production:
-
Flow - focus on moving material and information as close to customers as possible;
-
Value stream mapping - break down each stage of a process into discrete tasks and create a flowchart of the entire process;
-
Five S's, Sort, Set in Order, Shine. Standardize. and Sustain.
-
Kanban - visual cues such as stickers or colored tape can be used to track inventory.
-
Theory of constraints: Identify bottlenecks and use lean tools such as kanban boards to eliminate them.
-
Just-in time - Get components and materials delivered right at the point of usage;
-
Continuous improvement - Make incremental improvements rather than overhauling the entire process.